The Internet of Things has revolutionized the way devices interact, collect data, and automate processes. One of the core components of IoT systems is the use of sensors and actuators. While they both play a crucial role in enabling smart automation, they serve distinct functions. Understanding the difference between IoT sensors and actuators in IoT can help businesses and developers create more efficient and reliable IoT applications.
What Are IoT Sensors?
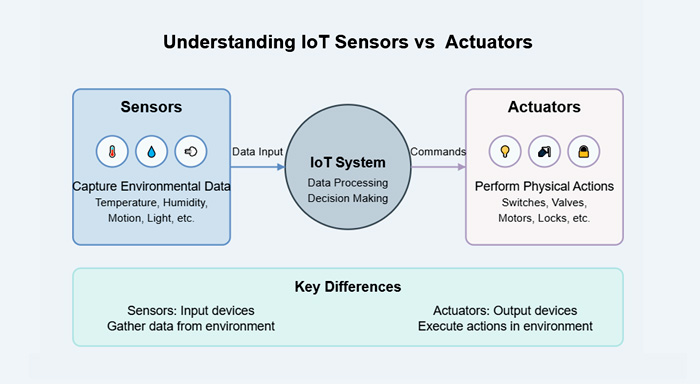
IoT sensors are devices that detect and measure physical parameters from the environment. These parameters can include temperature, humidity, motion, light, pressure, and more. Sensors convert these physical signals into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to an IoT system for analysis and processing.
For example, in a smart home system, temperature sensors can detect room temperature and send the data to a central controller, which then determines if adjustments are needed to maintain comfort levels.
Some common types of IoT sensors include:
- Temperature sensors—measure heat levels in an environment.
- Motion sensors—Detect movement and presence.
- Light sensors—Monitor light intensity for automatic brightness control.
- Pressure sensors—Measure force or stress applied to an object.
- Proximity sensors—Detect the presence of objects without direct contact.
Sensors are essential for collecting real-time data that can be used to monitor conditions, trigger actions, and optimize processes in various industries, from healthcare to industrial automation.
What Are Actuators in IoT?
While sensors gather data, actuators in IoT take action based on the processed data. An actuator is a device that receives signals from an IoT system and performs a physical action, such as opening a valve, turning on a motor, or adjusting a thermostat.
For instance, in a smart irrigation system, moisture sensors detect the soil’s dryness level. If the moisture level is too low, the actuator (e.g., a water pump) will be activated to irrigate the soil until optimal conditions are met.
Common types of actuators include:
- Linear Actuators—Provide motion in a straight line.
- Rotary Actuators—Enable rotational movement.
- Hydraulic Actuators—Use liquid fluid power for motion.
- Pneumatic Actuators—Utilize compressed air to create movement.
Actuators help execute automated processes, reducing the need for human intervention and improving efficiency in smart devices and industrial applications.
Key Differences Between IoT Sensors and Actuators

How Sensors and Actuators Work Together in IoT
IoT sensors and actuators in IoT work in tandem to enable automation and smart functionalities. The process follows these steps:
- Sensing: Sensors collect real-world data (e.g., temperature, humidity, motion).
- Data Processing: The collected data is analyzed by an IoT platform or cloud system.
- Decision Making: Based on predefined rules or AI algorithms, the system decides on an appropriate response.
- Actuation: Actuators execute the necessary physical actions (e.g., turning on a fan or closing a valve).
For example, in a smart factory, vibration sensors on machines can detect irregularities and send alerts. If a critical issue is identified, an actuator might shut down the machine to prevent damage or accidents.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between IoT sensors and actuators in IoT is essential for designing efficient smart systems. Sensors collect crucial data, while actuators perform actions based on this data, ensuring smooth automation and control. Whether in industrial automation, healthcare, smart homes, or agriculture, the seamless integration of sensors and actuators is what makes IoT truly intelligent and effective.
Related Posts: