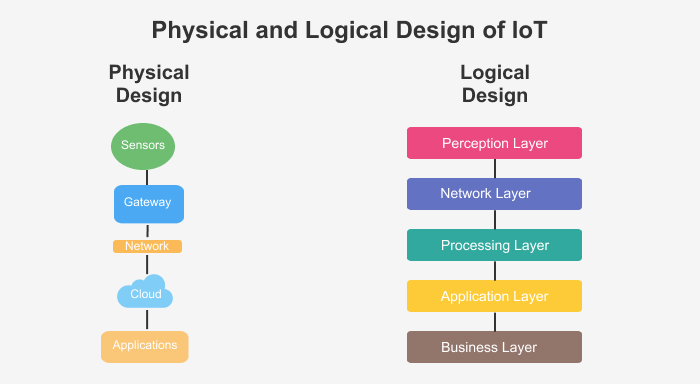
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing industries by enabling seamless connectivity between devices, systems, and users. The logical and physical design of IoT plays a critical role in defining how IoT systems function efficiently. While the physical design focuses on tangible components, the logical design deals with the conceptual and structural aspects of IoT networks. Understanding these two perspectives is essential for building robust and scalable IoT architectures.
Physical Design of IoT
The physical design of IoT refers to the hardware components that form the backbone of an IoT system. These components include:
- IoT Devices and Sensors
- Edge Devices and Gateways
- Connectivity Modules
- Cloud and Data Storage
Logical Design of IoT
The logical design of IoT focuses on how data moves and interacts within an IoT system. It encompasses the following aspects:
- Architecture Models
- Three-Layer Architecture
- Five-Layer Architecture
- Edge-Fog-Cloud Architecture
- Three-Layer Architecture
- Data Flow and Communication
- Security and Encryption
- Application and Service Integration
Comparative Analysis of IoT Architectures
Different IoT architectures adopt varied approaches to physical and logical design. Here’s a comparative analysis:
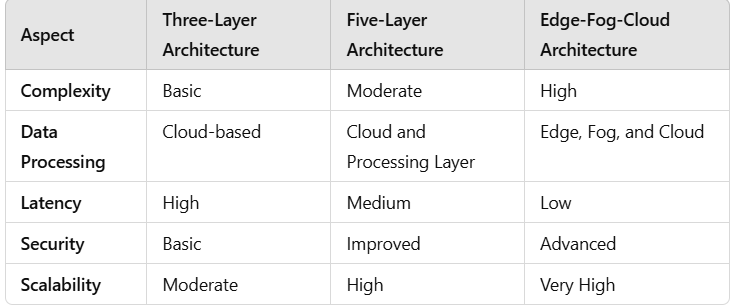
The three-layer architecture is suitable for small-scale applications, while the five-layer model enhances functionality by adding processing and business intelligence. The edge-fog-cloud model is ideal for real-time and large-scale IoT implementations due to its distributed computing capabilities.
Conclusion
The physical and logical design of IoT is fundamental to the success of an IoT ecosystem. While the physical design ensures proper hardware integration and connectivity, the logical design governs data flow, security, and decision-making. Choosing the right architecture depends on factors such as scalability, security requirements, and latency constraints. As IoT continues to evolve, innovative architectures will further enhance efficiency, intelligence, and real-time capabilities across industries.
Related Post:
How IoT Works: A Step-by-Step Guide